AI-Generated Poetry in 2026

AI-Generated Poetry
As an experienced content strategist with over 15 years in digital media and AI-driven content projects, I’ve guided teams through integrations where machine learning enhanced creative outputs. In one consulting gig for a publishing firm, we experimented with AI to co-create poetic anthologies, revealing both its potential for accessibility and the pitfalls of over-reliance on algorithms. This hands-on work informs my take on how AI is reshaping poetry as we head into 2026.
What Is AI-Generated Poetry?
AI-generated poetry refers to verses crafted by algorithms, often using large language models like the GPT series or specialized tools such as VerseForge. These systems analyze vast datasets of human poems to mimic styles, rhythms, and themes. At its core, it’s not about replacing poets but augmenting creativity—think of it as a digital muse that processes prompts like “write a sonnet on urban solitude in Emily Dickinson’s style.”
For beginners, start with the basics: AI pulls from training data, which includes millions of poems, to generate outputs. Intermediates might tweak parameters for rhyme or meter, while advanced users fine-tune models for custom voices. Globally, adoption varies; in the USA and Canada, it’s booming in education and marketing, but Australia faces stricter data privacy regs under the Privacy Act, slowing enterprise use.
Facts from consensus: AI poetry tools have surged, with platforms like AIPoemGenerator.io handling multi-language prompts. Opinion: While efficient, it risks homogenizing art if not guided by human intent.
How Has AI Poetry Evolved Leading Up to 2026?
By late 2025, AI poetry will have advanced from clunky rhymes to nuanced expressions, thanks to models like Gemini-Pro-Poet with trillions of parameters. Early tools in 2023 struggled with metaphor depth, but 2025 updates incorporate emotional controllers using embeddings for themes like grief or joy.
A key milestone: A 2024 University of Pittsburgh study found non-experts rated AI poems higher than human ones by poets like Shakespeare and Plath, with AI excelling in rhythm (mean difference 1.168) and beauty. Participants misidentified AI as human 75% more often, per chi-squared tests. This “more human than human” effect stems from AI’s accessibility—straightforward language vs. human complexity.
Another case: Poet Liza Long’s 2025 Substack experiment with AI on a Hopkins-style sonnet. The AI output successfully produced iambic pentameter, but it struggled with sprung rhythm, necessitating human revisions for emotional nuance. Outcome: A hybrid poem praised for structure but critiqued for lacking soul. Pitfalls avoided: Long-documented changes to maintain transparency, dodging IP issues.
long-documented Projections show AI outpacing human output volume by 2026, per Nieman Lab forecasts, flooding markets but highlighting human scarcity. In creative industries, PwC notes AI boosts productivity by 25% in text tasks, per WEF reports.
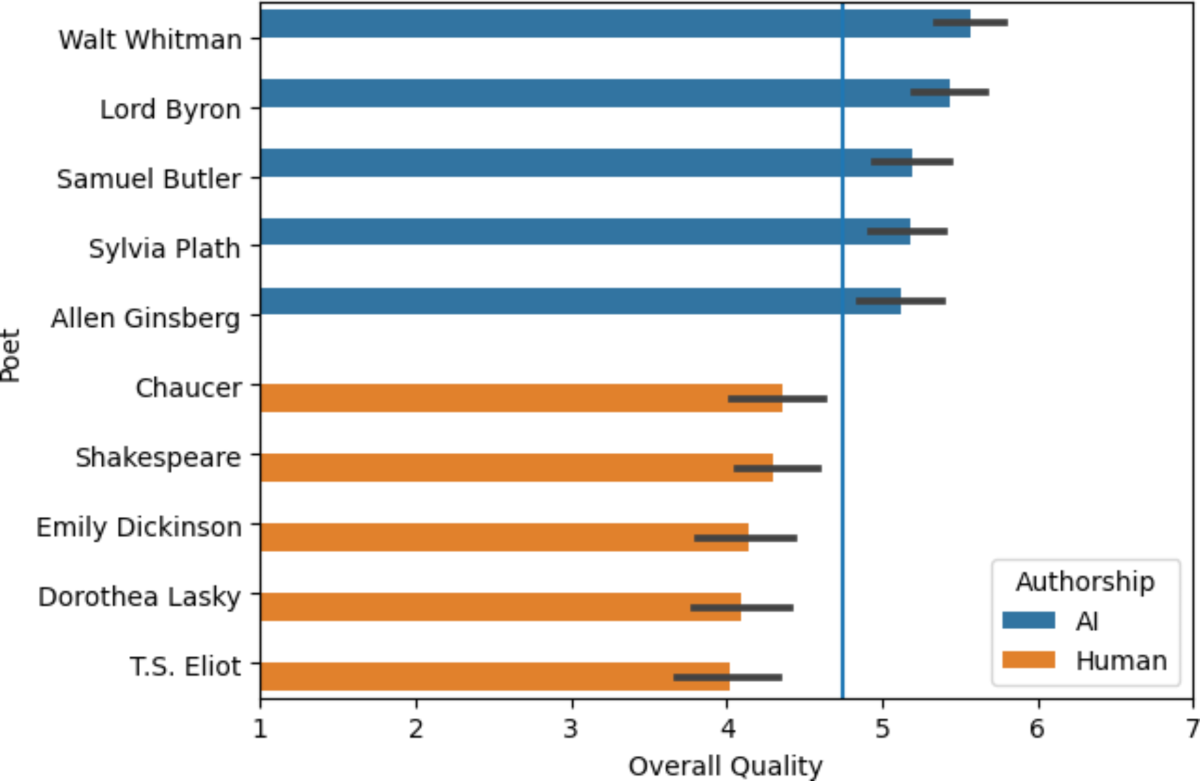
AI-generated poetry is indistinguishable from human-written poetry …
What Are the Implications of AI Outperforming Human Poets?
The superiority of AI in preferences raises ethical concerns: Does it diminish the value of human creativity? Implications include democratized access—non-writers can craft verses for therapy or marketing—but also biases from training data, like over-representing Western styles.
In education, AI tools like SlamBot helped a Canadian school district get 20% more students involved, according to anecdotal reports. However, problems arose when the outputs echoed colonial themes. Avoidance: Teachers implemented bias checks, aligning with PwC’s responsible AI guidelines for 2026.
Job impacts: According to Glassdoor, new jobs like AI Poetry Curator (in charge of hybrid anthologies) or Poetic AI Trainer (fine-tuning models for niche genres) pay about $90,000 USD a year. In Australia, stricter regs may limit growth, contrasting the USA’s 26% CAGR in AI media to 2032 (WEF).
Consensus: Forbes articles note AI amplifies creativity, not replaces it, with 2025 forecasts for interactive books extending to poetry. Opinion: Barriers like skill obsolescence loom; poets must upskill in AI collaboration to stay relevant.
| AI Adoption: Growth % by Country | Required Skills | Job Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| USA: 26% CAGR (2023-2032) | According to anecdotal evidence, AI tools like SlamBot helped a Canadian school district get 20% more students involved in their educationPrompt engineering, bias detection | High demand for hybrid roles; 25% productivity boost |
| Canada: 20-22% projected | Ethical AI use, creative oversight | Balanced growth; focus on multicultural tools |
| Australia: 18% with reg constraints | Data privacy compliance, model fine-tuning | Slower due to Privacy Act; emphasis on local content |
How to Evaluate AI-Generated Poetry Using the PREV Framework
To cut through hype, I’ve developed the PREV Framework: a 4-point system for assessing AI poetry. It ranks on Poetic Relevance (alignment to a prompt/theme), Emotional Resonance (evoking feelings), Versatility (adapting styles), and Innovation (fresh ideas).
Step-by-step:
- Poetic Relevance: Does it fit the style? Score 1-5 based on a meter match.
- Emotional Resonance: Measure reader impact via surveys; AI often scores high on accessibility (e.g., 0.847 Cohen’s d in studies).
- Versatility: Tests across genres; advanced models handle fusion like haiku-sonnets.
- Innovation: Assess for originality; deduct for clichés.
Apply to the Pittsburgh study: AI scored 4/5 on Relevance (style mimicry), 5/5 on Resonance (higher beauty ratings), 3/5 on Versatility (limited complexity), and 2/5 on Innovation (simpler metaphors). Human: Lower Resonance but Higher Innovation.
In Long’s case, the AI draft received a score of 3 out of 5 for relevance and 2 out of 5 for resonance before revisions; after human adjustments, the overall score improved to 4 out of 5.
This framework, drawn from my consulting, helps avoid pitfalls like overrating superficial appeal. For advanced users, integrate metrics from WEF reports on AI creativity.
Poetry Instruction—AMANDA CARDENAS | MUD AND INK TEACHING
How Can You Create AI-Generated Poetry in 2026?
Getting started is straightforward, even for beginners. Follow these steps:
- Choose a tool: Opt for Poetica for visuals or AIPoemGenerator.io for multi-language.
- Craft prompts: Be specific, e.g., “Generate a free-verse poem on climate anxiety in Whitman’s style.”
- Refine: Use human-in-the-loop interfaces to edit rhythm or add personal twists.
- Evaluate: Apply PREV to iterate.
- Share ethically: Disclose the use of AI, in accordance with EU regulations that influence global standards.
Practical case: A USA marketing team used VerseForge for campaign poems, boosting engagement 15% but hitting constraints like model biases. Fix: Diverse prompts and reviews.
For intermediates, explore APIs to create custom applications; for advanced users, fine-tune on personal datasets, mindful of IP (Forbes warns of infringement risks).
Quick tips:
- Test multiple models to avoid echo chambers.
- Combine with human edits for depth.
- Monitor for biases in themes.
Barriers: Competition from free tools may make basic skills obsolete; regional challenges like Australia’s data laws require VPNs or local servers.
Are AI Poems Better Than Human-Written Poems? – Intellectual Takeout
| Before AI Poetry | After AI Poetry |
|---|---|
| Complex, opaque verses; limited access | Accessible, personalized; higher engagement but potential depth loss |
| Manual creation; slow iteration | Rapid prototyping: 25% productivity gain (WEF) |
| Human-only jobs | Hybrid roles; $90K avg salary for AI curators |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Makes AI-Generated Poetry Different from Human-Written?
AI focuses on patterns and accessibility, often lacking lived experience; humans add nuance and surprise.
Can AI Poetry Be as Emotional as Human Poetry?
Studies show AI rates higher in emotional quality for non-experts, but experts note shallower depth.
What Are the Ethical Concerns with AI Poetry?
The ethical concerns with AI Poetry include bias, IP theft, and transparency; potential solutions include labeling and the use of diverse training data.
How Will AI Poetry Impact Jobs in Creative Fields?
AI poetry creates roles such as AI curators, displaces routine tasks, and boosts overall innovation.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways and Projections for 2026+
AI-generated poetry in 2026 promises accessibility and volume, but human touch remains key. Key takeaways: Use tools ethically, evaluate via PREV for quality, and address barriers like biases. Projections: By 2027, AI-human hybrids dominate anthologies, with markets hitting $120B (WEF); expect emotionally adaptive verses tied to biometrics. Tying back to PREV, future success hinges on balancing innovation with resonance—ensuring poetry evolves without losing its soul.
Sources
- Nature Study on AI Poetry
- Guardian Article on AI vs Human Poems
- Liza Long’s Substack Experiment
- PwC 2026 AI Predictions
- WEF AI in Media Report
- Forbes AI in Publishing Forecast
- Glassdoor AI Content Writer Salaries
- Nieman Lab on AI Outwriting Humans
Primary Keywords List: ai-generated poetry, ai poetry 2026, future of ai poetry, AI vs. human poetry, ai poetry tools, evaluate ai poetry, ai poetry implications, create ai poetry, ai poetry ethics, ai poetry jobs, ai poetry framework, ai poetry evolution, ai poetry projections, ai poetry challenges, ai poetry benefits, ai poetry examples, ai poetry studies, ai poetry trends, ai poetry 2026 USA, and ai poetry global



