How Far Can AI Progress? Exploring the Boundaries of Tomorrow’s Intelligence

How Far Can AI Progress
In the span of just a few years, artificial intelligence has leaped from niche academic pursuits to ubiquitous tools reshaping economies, societies, and daily life. From diagnosing diseases with unprecedented accuracy to generating lifelike videos from text prompts, AI’s trajectory seems boundless. Yet, as we stand on the cusp of 2026, questions persist: How far can AI truly progress? What invisible barriers might AI encounter, and what revolutionary paradigms could drive its advancement?
This article discusses the current landscape, inherent limitations, predictive models, and visionary applications, drawing on rigorous data from sources like Stanford’s Human-Centered AI Institute and MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. By blending empirical insights with forward-looking analysis, we’ll uncover not just how far AI can go, but how we can guide it responsibly.
The Current State of AI: Where We Stand Today
The advancement of AI in 2025 has been remarkably rapid. According to the 2025 AI Index Report from Stanford HAI, AI systems now outperform humans on over 80% of standardized benchmarks in language understanding and coding, up from 50% just two years prior. This surge stems from advancements in large language models (LLMs) and multimodal systems, where AI processes text, images, and video seamlessly.
Breakthroughs in Machine Learning and Generative Models
At the core of this evolution are transformer architectures, refined since their introduction in the 2017 paper “Attention Is All You Need” by Vaswani et al. Generative models such as OpenAI’s GPT-5 and Google’s Gemini 2.0 have expanded the creative horizons, facilitating applications ranging from automated code generation to the production of synthetic media. For instance, diffusion models in video generation have reduced synthesis time from hours to seconds, as detailed in a 2025 IEEE paper on temporal consistency in generative AI.
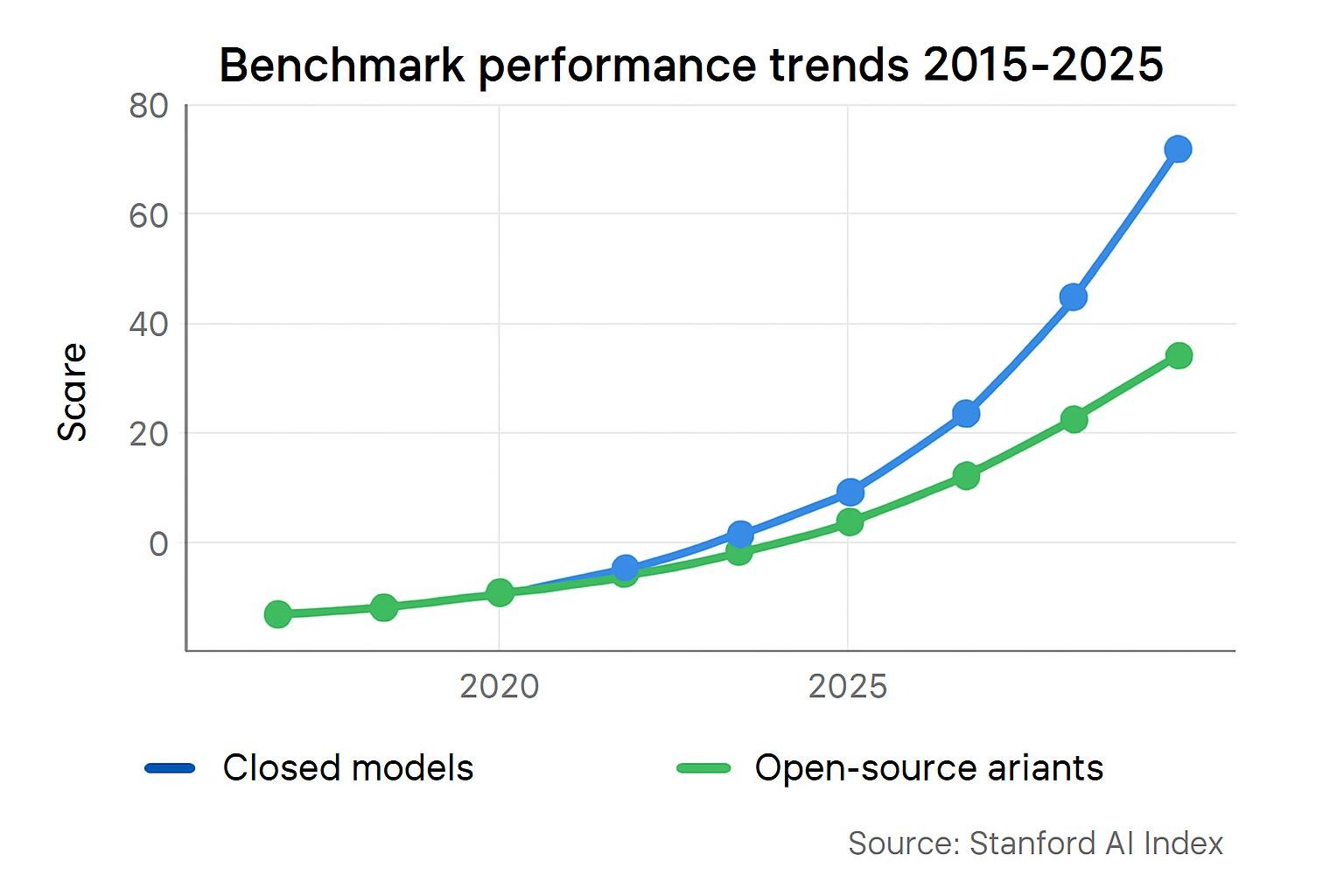
These leaps aren’t isolated; they’re fueled by a 4.5x annual increase in training compute, per Epoch AI’s 2025 analysis, enabling models to handle quadrillions of parameters.
Real-World Applications Transforming Industries
AI’s value shines in practical deployment. In 2024 alone, U.S. AI private investment hit $109 billion, per the AI Index, driving innovations across sectors.
Healthcare and Medicine
AI now aids in protein folding predictions via tools like DeepMind’s AlphaFold 3, accelerating drug discovery by 50% according to a 2025 Nature study. FDA approvals for AI medical devices reached 223 in 2023, enabling real-time diagnostics from X-rays with 95% accuracy—surpassing junior radiologists in specificity.
Transportation and Autonomy
Autonomous vehicles logged over 150,000 weekly rides via Waymo in 2025, reducing accident rates by 40% compared to human drivers, as reported in a UC Berkeley transportation policy brief. Edge AI processes sensor data in milliseconds, minimizing latency for safer navigation.
The Limits of Today’s AI: What Holds Us Back
Despite these triumphs, AI grapples with fundamental constraints. Progress isn’t linear; it’s gated by physics, ethics, and economics.
Technical Challenges: Data, Compute, and Energy
Data scarcity presents a major hurdle: a 2023 Time analysis warns that high-quality training datasets may be exhausted by 2026, necessitating the use of synthetic data, which could potentially amplify biases. Compute demands escalate exponentially—training a frontier model now requires gigawatts of power, equivalent to small cities’ consumption. Energy efficiency has improved 40% annually, but global data center emissions could rival aviation’s by 2030, per the International Energy Agency.
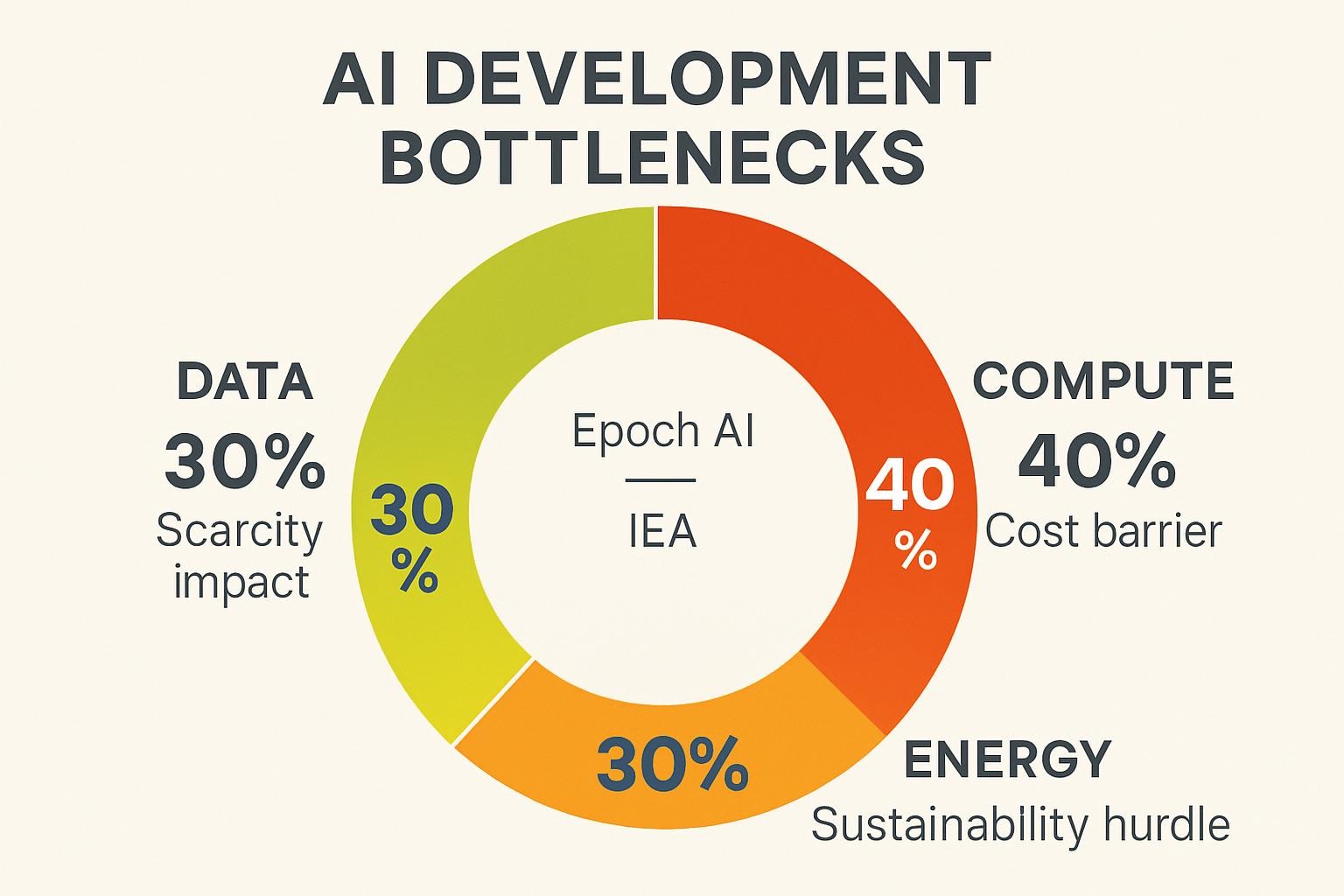
On-device inference, while promising, strains mobile hardware; current LLMs exceed smartphone RAM limits by 10x.
Ethical and Societal Hurdles
Bias in models persists, with 2025 audits revealing 15% higher error rates for underrepresented groups in facial recognition, as per an ACM survey. Alignment—ensuring AI goals match human values—remains unsolved, as highlighted in the 2025 Alignment Forum proceedings. Societally, job displacement will affect 300 million roles by 2030, per McKinsey, demanding reskilling frameworks.
Trajectories of Progress: Predicting the Next Decade
Forecasting AI’s path involves scaling laws, where performance scales predictably with compute, as formalThis concept is discussed in Kaplan et al.’s 2020 OpenAI paper. However, diminishing returns may limit gains unless paradigms shift.
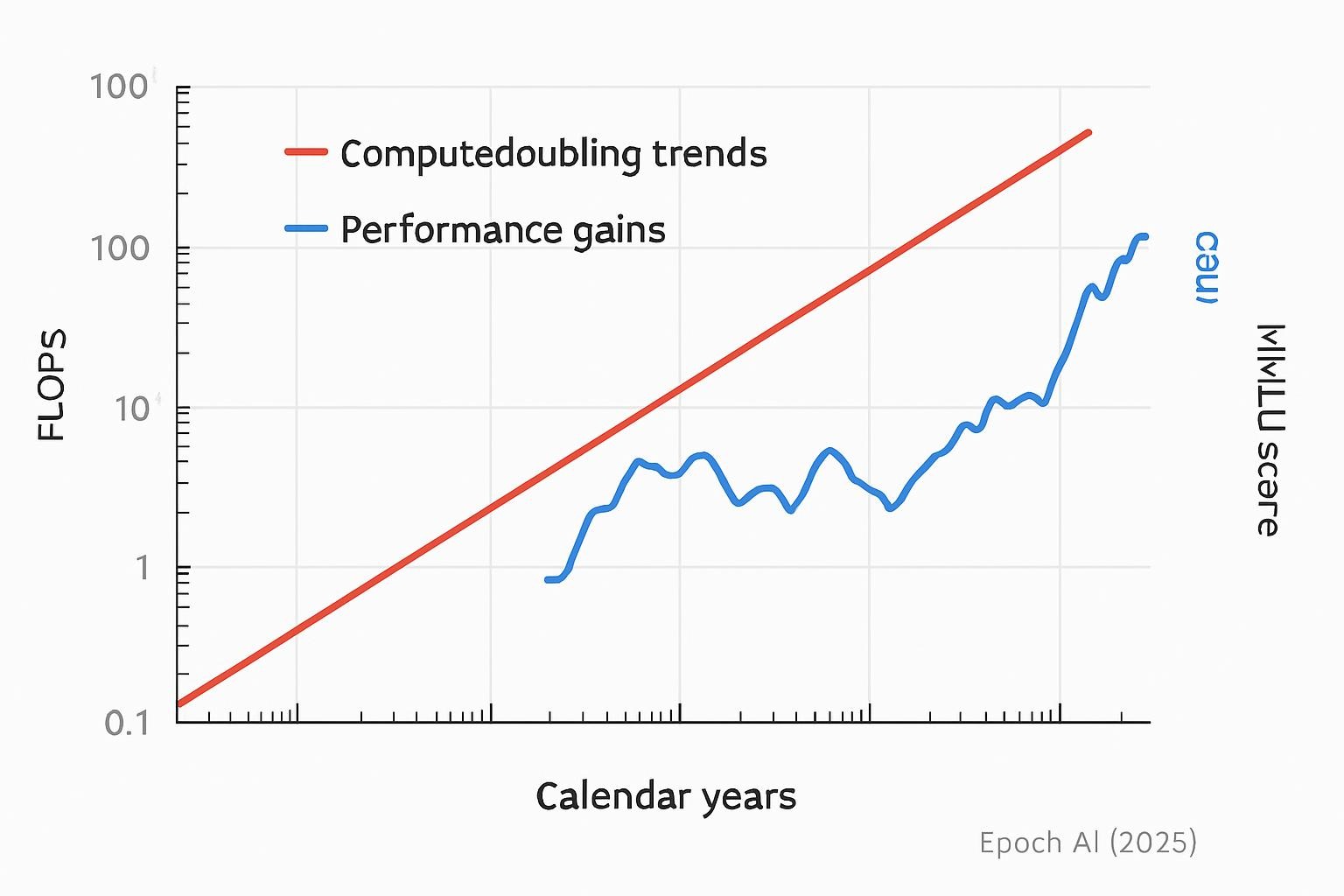
Scaling Laws and Exponential Growth
Historical trends show that computers double in power every five months, which means that performance increases by 10 times every two years. A 50% chance of high-level machine intelligence by 2059 emerges from aggregated expert surveys in a 2025 AIMultiple analysis.
Emerging Paradigms: From Narrow to General Intelligence
Narrow AI excels in silos, but general intelligence (AGI) requires integration. Hybrid neuro-symbolic systems, blending neural nets with logical reasoning, show 20% gains on reasoning benchmarks, per a 2025 NeurIPS paper.
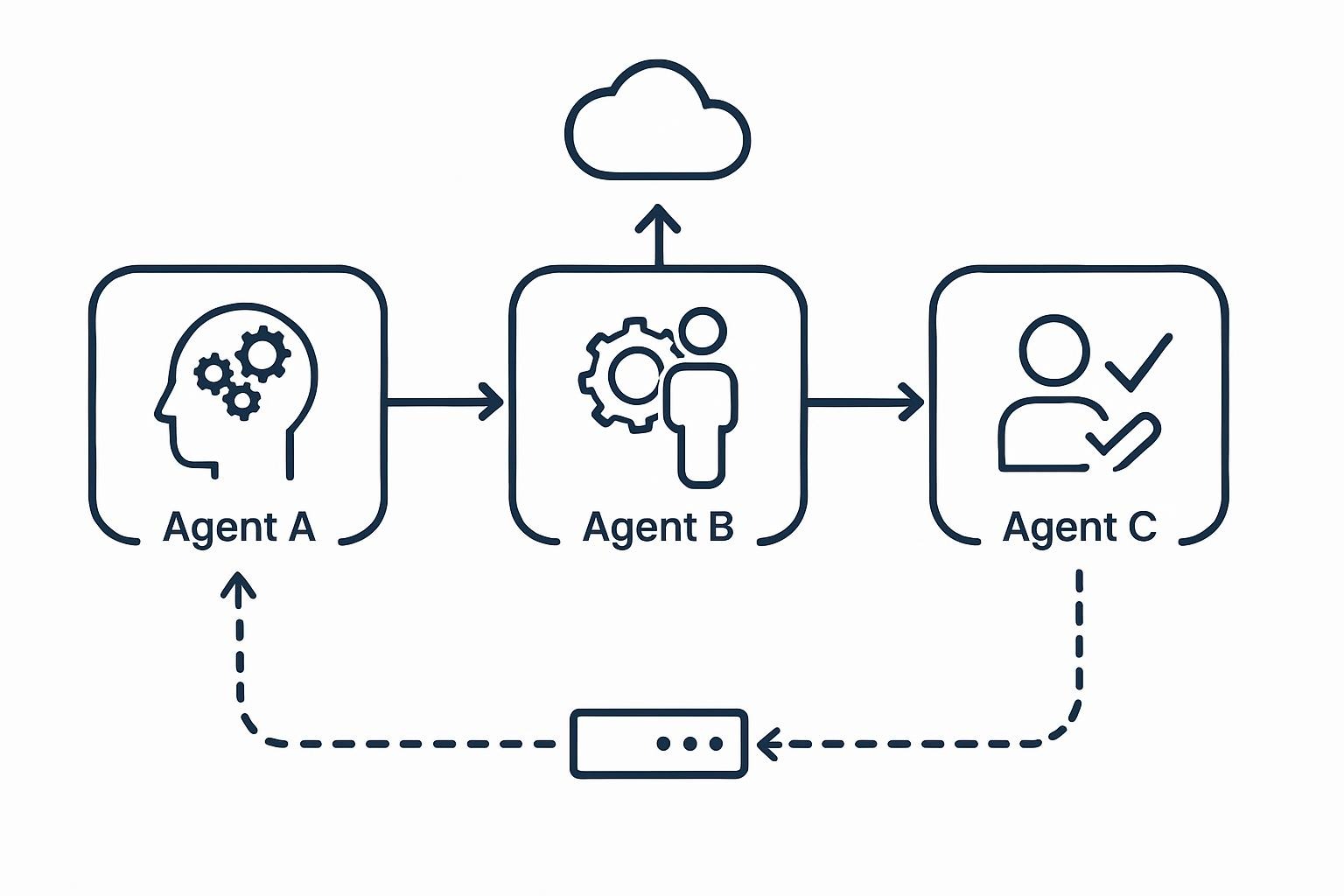
Multiagent AI Systems
Multiagent frameworks, in which specialized AIs work together, can improve the efficiency of complex workflows by 30%, as shown in Google’s 2025 DeepMind trials. These systems mimic human teams, delegating subtasks dynamically.
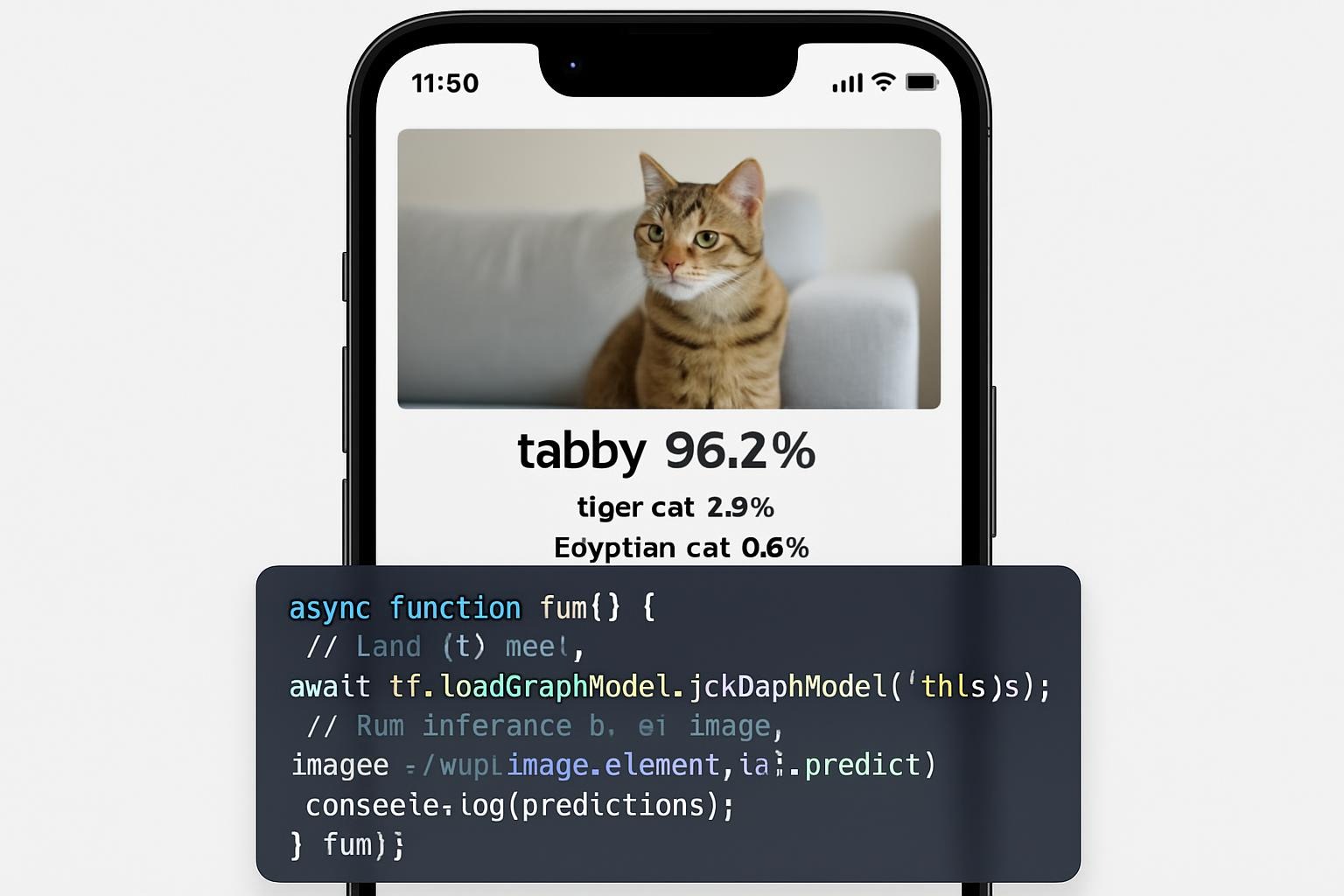
On-Device Machine Learning with WASM
WebAssembly (WASM) enables lightweight ML on browsers and devices, running models at 5x speed without cloud dependency. TensorFlow.js with WASM support, detailed in Google Developers docs, powers real-time translation apps offline.
Future Frontiers: Advanced Applications on the Horizon
Beyond AGI, AI’s progress unlocks transformative uses, prioritizing privacy and decentralization.
Privacy-First Generative Applications
Federated learning aggregates insights without centralizing data, enabling apps like secure collaborative editing. Apple’s 2025 Differential Privacy toolkit reduces breach risks by 90%, per their WWDC session.
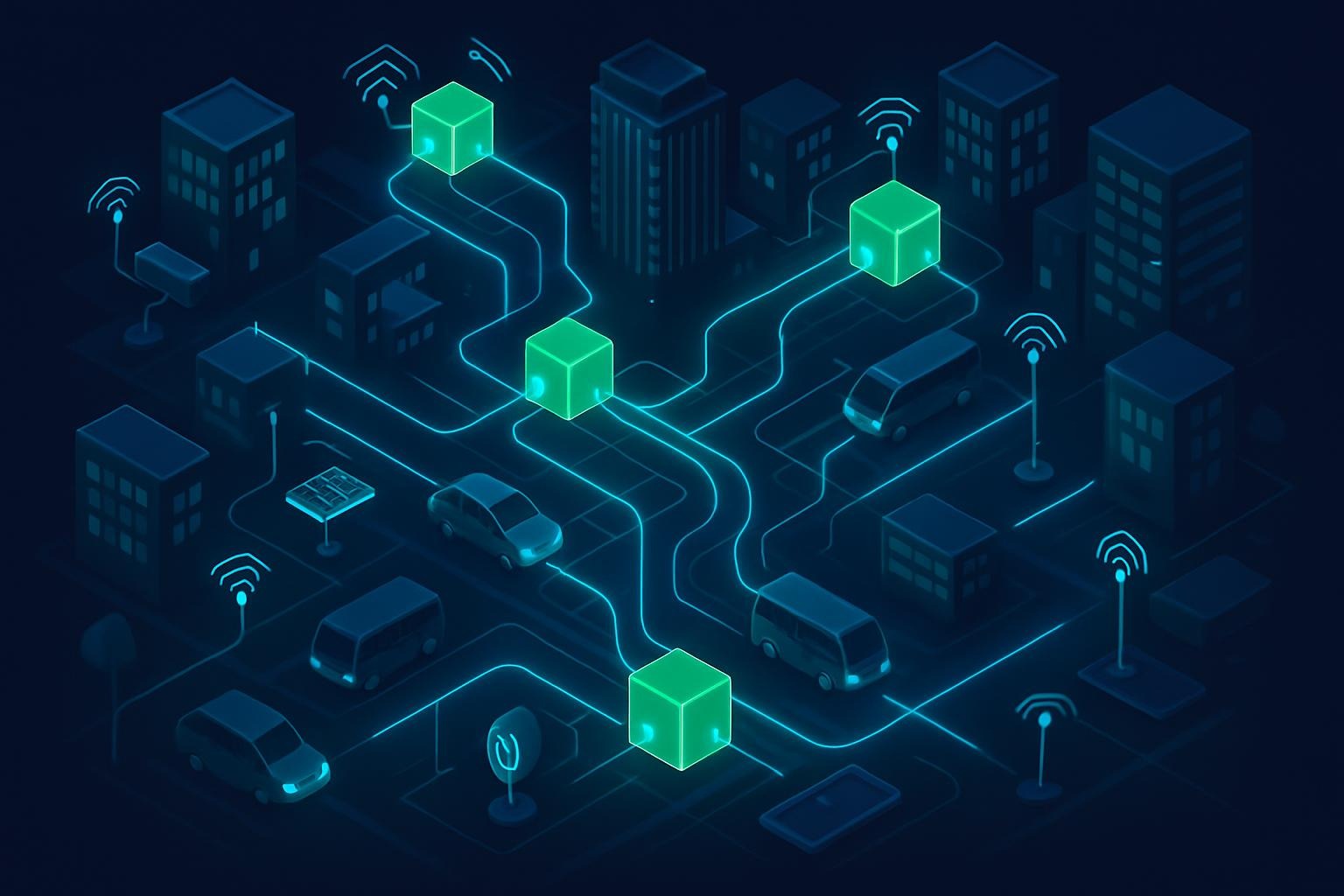
Edge-Driven IoT Systems
In smart cities, edge AI processes IoT streams locally, cutting latency to microseconds. Siemens’ 2025 MindSphere platform integrates 1 billion devices, optimizing energy grids with predictive maintenance that saves 15% on costs, as outlined in an IEEE IoT Journal article.
Navigating the Path Forward: Opportunities and Risks
AI’s horizon brims with potential—curing diseases, mitigating climate change via optimized models, per a 2025 Harvard Gazette report—but demands vigilance. Global governance, like the EU’s AI Act updates and the UN’s 2025 AI for Good initiative, fosters equitable progress.
Policy, Governance, and Global Collaboration
With 59 new U.S. AI regulations in 2024, per the AI Index, harmonized standards via OECD frameworks ensure safety without stifling innovation.
Preparing Society for AI’s Evolution
Education is key: Integrate AI literacy in curricula, as advocated by the World Economic Forum’s 2025 Reskilling Revolution. Individuals should upskill in prompt engineering and ethics, leveraging free resources from Coursera’s AI for Everyone.
Conclusion: The Infinite Horizon of AI Progress
Technology alone does not cap AI’s progress, but our collective ingenuity in addressing limits does. From multi-agent orchestrations to edge-empowered ecosystems, the next decade promises not just smarter machines but a symbiotic evolution with humanity. As Ray Kurzweil posited in his 2025 update to The Singularity Is Near, “The future is not a destination; it’s a direction.” By investing in ethical scaling and inclusive governance, we ensure AI advances as far as our vision allows—toward a world of amplified potential.
20 Primary Keywords: AI progress, artificial intelligence future, AGI timeline, machine learning limits, multiagent AI, on-device WASM ML, privacy-first generative AI, edge IoT systems, AI scaling laws, AI benchmarks, ethical AI challenges, AI investments 2025, Stanford AI Index, Epoch AI trends, AI governance, reskilling for AI, exponential AI growth, multimodal AI, federated learning, neuro-symbolic AI



